- 1. An Introduction to Marketing Management
- 2. The Role of a Marketing Project Manager
- 3. Building a Marketing Team
- 4. How To Create a Marketing Strategy
- 5. How to Create a Marketing Plan: Ultimate Guide
- 6. How To Build a Marketing Calendar
- 7. An Introduction to MarTech
- 8. Choosing Marketing Tools & Software
- 9. A Guide to Marketing Analytics
- 10. How To Create a Marketing Dashboard
- 11. Marketing Resource Management Guide
- 12. FAQs
- 13. Marketing Glossary
- 1. An Introduction to Marketing Management
- 2. The Role of a Marketing Project Manager
- 3. Building a Marketing Team
- 4. How To Create a Marketing Strategy
- 5. How to Create a Marketing Plan: Ultimate Guide
- 6. How To Build a Marketing Calendar
- 7. An Introduction to MarTech
- 8. Choosing Marketing Tools & Software
- 9. A Guide to Marketing Analytics
- 10. How To Create a Marketing Dashboard
- 11. Marketing Resource Management Guide
- 12. FAQs
- 13. Marketing Glossary
What is marketing management?
Marketing management involves developing and implementing strategic marketing programs, processes, and activities that align with wider business objectives, while utilizing customer insights, tracking metrics, and optimizing internal processes to achieve success.
Being an effective marketing leader is more complex than it sounds. Speak to any marketing management professional and they’ll tell you that their work is equal parts strategy, planning, execution, and analysis. It’s easy to see why. Marketing professionals with a documented strategy are 313% more likely to succeed when compared to their peers who do not have a documented strategy.
To help you succeed, we will take a close look at marketing management in this article. Read on to learn more about what marketing management is, the benefits of marketing management, different processes, and tips.
If you are looking for a 360-degree marketing tool to manage all the components of your marketing strategy, Wrike has the solution for you.
Marketing management is centered on creating, planning, and implementing strategies that will help achieve wider business objectives. These business objectives can involve increasing brand awareness, boosting profits, or entering previously untapped markets. When we begin to consider the field of marketing management, it’s important to look to marketing experts Philip Kotler and Kevin Lane Keller, who, in their book “Marketing Management," offer a standard marketing management definition as “the development, design, and implementation of marketing programs, processes, and activities that recognize the breadth and interdependencies of the business environment.”
Managers need to study their customers, have a deep understanding of the methods and strategies that retain and delight them, and be active in measuring achievements and optimizing internal processes.
Think of it this way: a high school teacher does not simply teach. They have to understand their students, create methods and strategies for passing on information, and track student progress through metrics and achievements.
In marketing, the right processes should elevate a brand, establish a strategically planned vision for an organization, and coordinate resources to get it all done.
Why is marketing management important?
Marketing management is important for businesses because it ensures effective customer engagement, product appeal, and targeted campaigns that can increase profits and achieve business objectives. You could spend years getting a product ready to launch but without proper management, you would inevitably hit several stumbling blocks.
At the outset, marketing management ensures you understand what your customer desires, down to colorways and packaging. Without it, you might find your product doesn’t even appeal to customers.
After spending considerable time preparing your product or service to be released, the right processes ensure it reaches your target market via the right channels at the right time. Marketing management can take your business from average to profitable. This can be accomplished when a team is able to analyze customer profiles and market share ahead of time, as well as scrutinize campaign outcomes, team performance, ROI, and costs once the project is completed.
International marketing management
International marketing management encompasses marketing activities that take place across national borders. This requires the marketing manager to achieve a deep understanding of the customer base in any country where the product is marketed, including cultural nuances and demographics particular to that nation.
When you are marketing products in various other countries, you might need to engage with marketers in those localities, which will further expand your management remit. This could involve hiring employees in that country or a third-party marketing agency to better reach customers there.
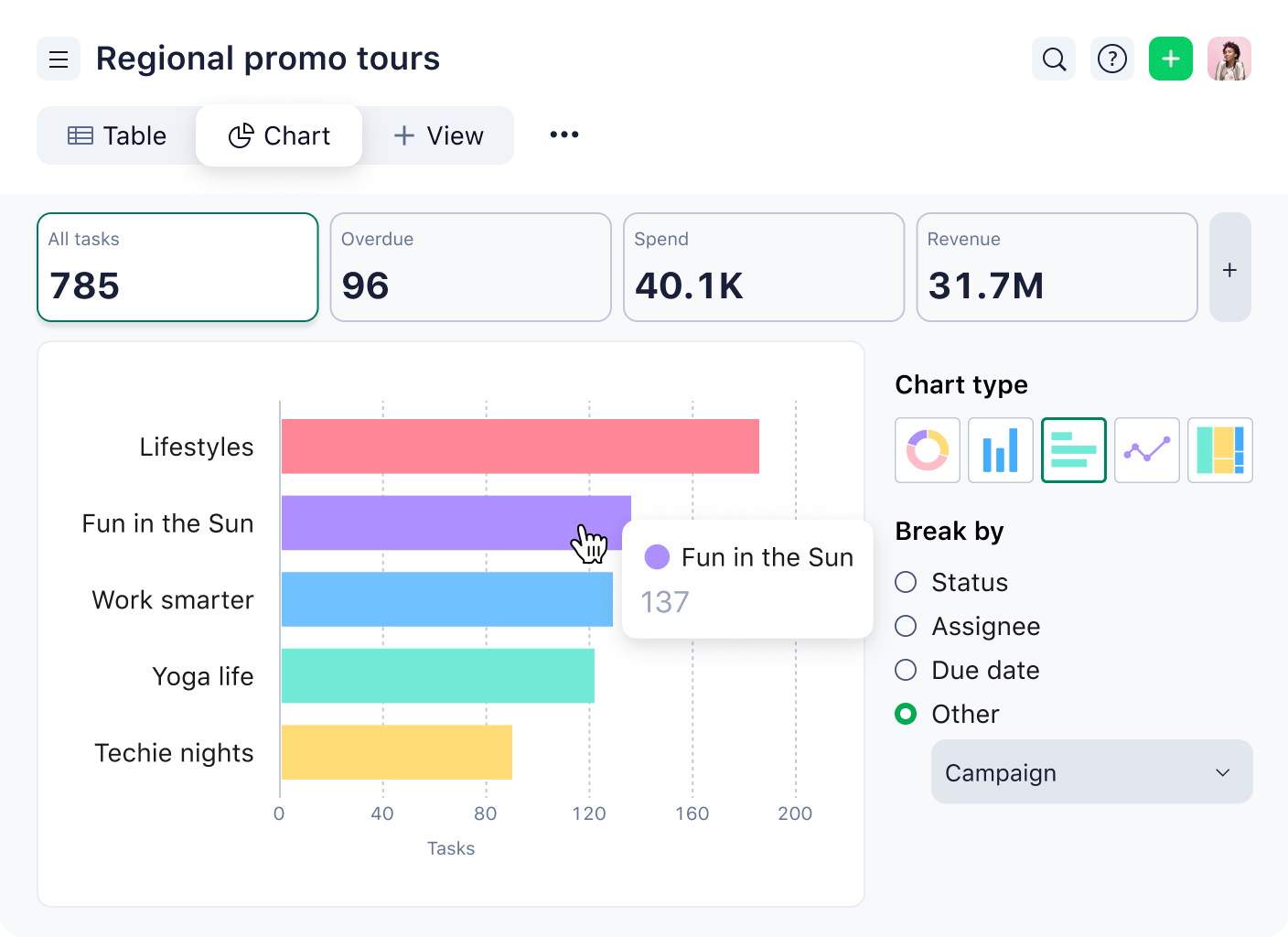

What are the 9 types of marketing management?
Marketing management spans a wide range of methods, strategies, and processes, which need to be coordinated effectively to ensure success. When weaved together, these elements will raise awareness of and generate ROI for your brand:
- Marketing strategy: Your organization’s plan for reaching prospects and converting them into customers
- Business development: Strategic initiatives such as mergers and acquisitions, business transformation, and entering new markets
- Brand management: Techniques to increase the perceived value of a brand over time
- Product development: The process of bringing a new product to market
- International marketing: Managing international distribution channels
- Media relations: Engaging with media and influencers to spread the word about your organization
- Customer marketing: Managing the customer experience to improve satisfaction and reduce churn
- Marketing operations: Managing marketing processes, technology, and data
- Sales: Generating leads, developing opportunities, and closing deals
What are the processes of marketing management?
Managers can use the following processes to optimize marketing efforts from all angles:
- Market and customer analysis: This process is all about understanding your organization’s current market position and analyzing consumer behavior.
- Development of strategy, goals, and objectives: Where does a business want to go? How does it plan to get there? After market and customer analysis, strategy will map the way forward.
- Product development: Marketing managers play a crucial role in product development. When it comes to articulating the benefits of a product, these professionals help craft poignant, on-brand messaging.
- Marketing program implementation: Once promising programs and campaigns have been identified, it’s time to deploy the right resources to launch them.
- Monitoring and control: Analyzing the success of marketing programs and activities is a crucial process. It informs how future activities will be planned and implemented.
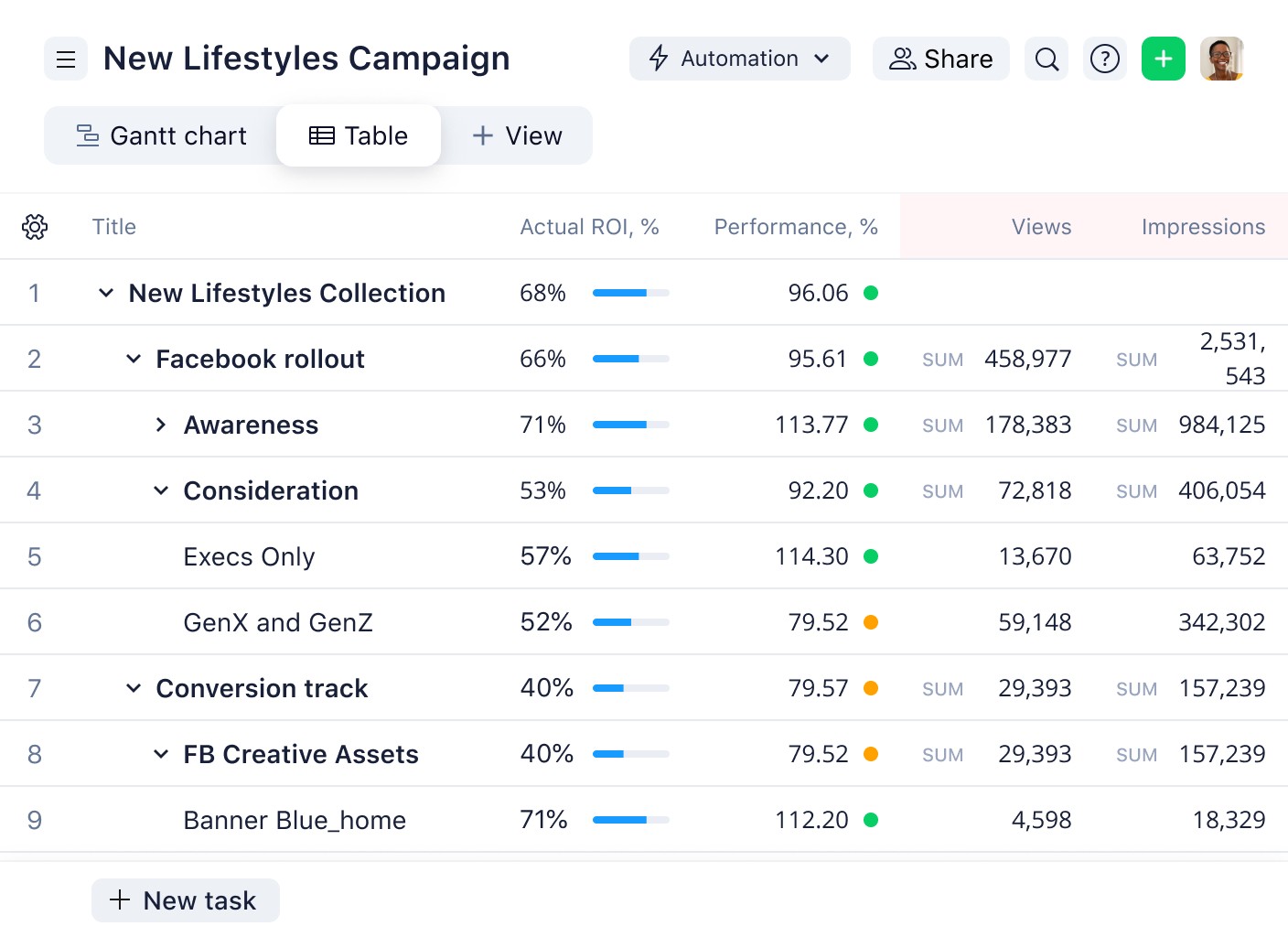

How is a marketing management strategy created?
While the marketing strategy involves the overall goals the company has with regard to reaching customers and markets, strategic marketing management involves creating a marketing plan to reach those goals and using a range of tools to ensure success is achieved.
Strategic marketing management often starts with a brand audit, which will allow a company to ask and answer several questions that can help direct the future strategy. A company should seek to understand the following about their present situation:
- How is its current brand strategy working?
- What are its strengths and weaknesses with regard to resources and expertise?
- What opportunities and threats does it face?
- How do its pricing and costs compare to competitors?
- What strategic issues might be facing the company?
A brand audit will allow a company to get a full picture of its competitive advantage in the market and any obstacles it needs to overcome in the future to maximize profitability. Once these questions are answered by relevant team members, strategic decisions can be made to create set goals and advance the company’s marketing vision.
The marketing management strategy is the set of activities required to meet the company’s marketing strategy goals and includes elements such as price points, product specifications, market location, and promotion. To develop this strategy, marketers will first need to have a strong understanding of the data around market share, customer profiles, and any past campaigns and marketing activities.
How is a marketing strategy implemented?
A marketing management strategy is implemented using a variety of methods, tools, and resources.
Activities of marketing management
To achieve these goals, the strategy must consist of a wide range of marketing channel management activities related to price, product, place, and promotion. This is widely referred to as the marketing mix. The job of the marketing manager is to adjust each of these elements in order to maximize sales and ROI.
These activities fall into the following categories:
- Price: Price is the monetary value placed on a product. It depends on production costs, the segment of customers targeted, and their ability to pay for the product, as well as demand for the product.
- Product: The product on the market needs to be optimized with target customers in mind for the remainder of the marketing mix to achieve the overall goal.
- Place: Place refers to both the general and exact locations customers are able to purchase a product. This involves making choices about online or brick-and-mortar availability, as well as the specific locations therein.
- Promotion: Finally, activities such as various advertising channels, direct marketing, press releases, and even incentives can all be utilized to promote the product once it has been optimized and produced.
What is the extended marketing mix?
The extended marketing mix is an extension of the above-outlined marketing mix. It looks specifically at service businesses, rather than physical products. Marketing management professionals can adjust these levers in order to optimize campaign success. In addition to price, product, place, and promotion, the extended marketing mix also includes the following:
- People: In businesses that deliver a service, employees are a critical component, and the amount of training or remuneration they receive is a component of the marketing mix.
- Process: Service industries rely on a set of processes to ensure customers receive a quality result, and processes can be tightened in order to maximize productivity and efficiency.
- Physical evidence: In service situations — for example, a hair salon — the physical location can be optimized for the customer’s experience in order to encourage better word-of-mouth marketing.
Deliver marketing campaigns with effortless collaboration
Philosophies of marketing management
There are a number of marketing management philosophies that determine marketing direction, stance, and activities. These philosophies are commonly called “marketing management concepts.”
These concepts have developed over time, but generally dictate the prioritization of marketing efforts.
- Production concept: Prioritizes production efficiency
- Product concept: Prioritizes the quality of the product(s)
- Selling concept: Prioritizes customer satisfaction
- Marketing concept: Prioritizes profits through customer satisfaction
- Societal concept: Prioritizes the societal impact of marketing activities
These concepts help marketing managers develop strategies and refine their approaches. They also dictate monitoring methods as each concept will have unique benchmarks and indicators of success.
Features of marketing management
Features of marketing management differ from the philosophies in that they describe the overall goals a strategy seeks to address. Features include:
- Helps to understand and satisfy the customer’s needs
- Assists in achieving the company’s overall goals
- Consists of a range of activities
- Facilitates successful exchanges between buyer and seller
The strategy must address the research and data collection that enables marketing teams to understand the customer’s wants, needs, and demands. Simultaneously, it needs to promote and advance the organization’s business goals and ultimately facilitate a successful exchange of goods between the organization and the customer.

What does a marketing manager do?
Depending on the size of the company, marketing management roles will vary in scope and responsibility, ranging from customer data analysis to managing a brand’s social media accounts.
In a small or medium business, marketing manager responsibilities may include all or some of the following:
- Setting goals and objectives for the marketing function of the company
- Researching the customer base in order to ascertain which segments of the market are ideal for the company’s campaigns
- Coordinating with third-party vendors for events, or with other departments for the completion of graphic design of materials
- Overseeing and controlling the marketing budget and making adjustments to ensure products and services are marketed appropriately
What are examples of marketing management?
In larger companies, marketing management roles can be extensive and involve large teams. Specialized roles can range from digital marketing manager to product marketing manager, and each role has different responsibilities that vary by marketing department.
Five examples of specialized marketing management roles:
- Digital marketing manager: A digital marketing manager develops, implements, and manages online marketing campaigns designed to promote a company’s products and services, and enhance its brand.
- Product marketing manager: A product marketing manager devises marketing plans to communicate features and benefits of new products to customers, delving into market research on product trends and serving as the voice of the customer within the company to ensure products are designed to suit customer needs.
- Brand marketing manager: A brand marketing manager ensures that brand messaging and imagery are utilized consistently across the company and plans ways to increase brand recognition in the market.
- Content marketing manager: A content marketing manager focuses on creating effective, valuable, and consistent content that highlights a company’s products or services to potential customers.
- Social media marketing manager: A social media marketing manager works specifically on optimizing social media communication and interactions for the company, including, but not limited to, Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
- Marketing campaign manager: A marketing campaign manager is responsible for the life cycle of a marketing campaign. They work closely with other departments, including sales, to execute campaigns and compile reports on their effectiveness.

What are some examples of marketing management tasks?
Each specialized marketing management role requires a host of different tasks, although there is some overlap depending on the size of the organization. Each organization will have a slightly different set of roles, depending on the company’s requirements.
- Digital marketing manager: A digital marketing manager sets goals and monitors targets for any digital campaigns they have planned. Oftentimes, they are in charge of creating and implementing strategies for pay-per-click advertising, social media advertising, email marketing campaigns, and text blast .
- Product marketing manager: A product marketing manager creates messaging to differentiate products from others in the market and articulate the product’s unique selling point, and conducts SWOT analysis, while also helping plan and execute new product launches and writing detailed case studies of client success to highlight to potential customers. They will also plan and execute marketing campaigns, oversee all elements of the campaign, and determine product price based on the company’s SWOT analysis.
- Brand marketing manager: A brand marketing manager works closely with graphic designers to ensure the company’s logo and brand guidelines are used properly. Daily tasks could include monitoring social media for trends and pitching stories to journalists with whom you’ve built relationships.
- Content marketing manager: A content marketing manager’s tasks typically include planning content campaigns, placing articles with news organizations, or collaborating with bloggers to amplify information about the product or service. Content marketing managers will also produce materials such as eBooks and blog posts, often with the goal of maximizing SEO opportunities and optimizing inbound marketing efforts.
- Social media marketing manager: A social media marketing manager plans campaigns for different channels, creates content via photography or video, and responds to questions or comments from potential or current customers.
- Marketing campaign manager: A marketing campaign manager plans and executes marketing campaigns, oversees all elements of the campaign, and delivers regular reports on its performance.
Where can I get marketing management training?
Marketing management is a popular degree, diploma, and training subject. Top-tier universities and institutions across the world offer BA, MSc, and program certifications in this subject.
It’s also possible to transition into a management role by having relevant work experience and qualifications. A keen marketer may choose to rise in their position and take supplemental marketing management training courses as a way of exploring this career path.
Of course, there is no better teacher than experience. As a marketer gains more knowledge and hands-on experience in the industry, they may find that a management role is simply a natural career progression for them.
What is the best marketing management software?
When it comes to deciding on the best marketing management software for your organization, it’s important to pinpoint the essential features for your team. A marketing manager likely needs software that enables them to:
- Create and organize documentation
- Track ongoing project progress each day
- Integrate with business intelligence tools such as Tableau
- Proof and approve marketing materials and assets
- Invite external stakeholders and clients to collaborate
- Wrike does all of this and more.
Wrike’s features enable 360-degree marketing management. From ideation to strategy, implementation, and monitoring, Wrike makes these processes easier and more efficient than ever.
Enable cross-functional collaboration to sync product and marketing efforts, track key marketing metrics and benchmarks for every campaign, and give in-context feedback that keeps all your objectives on track.
Learn more about how Wrike’s robust features could help support your marketing strategies. Grab a free two-week trial and see why more than two million customers choose Wrike.

Christine Royston
Christine is Wrike’s Chief Marketing Officer. She has more than 20 years of B2B enterprise marketing experience, having held senior leadership roles at Udemy, Bitly, Dropbox, and Salesforce. Christine is particularly skilled at building high-performing teams and creating marketing strategies that help organizations scale and transform.