Lean vs. Six Sigma: What Is the Difference?
The main difference between Lean and Six Sigma is that Lean prioritizes simplifying business processes by removing unnecessary steps, while Six Sigma relies on data and statistical analysis to fix and identify errors. Six Sigma focuses on minimizing mistakes, while Lean seeks to eliminate waste and create value.
Looking for a quick overview? Watch this short video to view the key difference between Lean and Six Sigma with examples.

Lean project management
Businesses adopt the Lean methodology in project management to simplify production and operations. The core focus of Lean is on eliminating redundant and unproductive steps in the development phase, leaving only necessary processes that run smoothly and efficiently to achieve the organization’s goals.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma in project management focuses on improving the quality and efficiency of processes and workflows. The core focus of Six Sigma is to minimize errors and waste by optimizing operations and performance. Six Sigma is integral to organizational leadership, and its widespread adoption helps companies deliver positive, quantifiable outcomes.
What is the difference between Lean and Six Sigma?
We’ve briefly discussed the main difference above, but let’s dive into a more comprehensive comparison of Lean vs. Six Sigma. To do this, we can break down the various factors that differentiate the two methodologies:
Waste
In Lean methodology, waste is defined as any process or activity that does not add value to the customer. Lean practitioners strive to improve processes to produce more customer value.
According to Six Sigma, a variation within a process causes waste. Six Sigma advocates strive to remove faults in processes by lowering variability.
Approach
Lean is a mindset that, when applied holistically, improves decision making. Lean practitioners prioritize continuous process improvement to seek methods that enhance value and reduce waste. It’s most successful when ingrained in an organization’s culture and implemented from the ground up.
Six Sigma is a deliberate, disciplined technique for solving organizational challenges by lowering risk and process variability. The Six Sigma certification program is one of the most well-known aspects of the methodology. Six Sigma professionals may be found at many levels of a business.
Leadership
Lean offers more flexibility, pushing its practitioners (including individual contributors and managers) to think big and tackle organizational challenges. Lean is well suited to independent organizational structures that facilitate cooperation across teams and hierarchies.
The Six Sigma methodology provides a structured, hierarchical leadership paradigm suited for highly organized companies. It equips professionals to carry out a specific function in their organization, typically beginning with localized issue resolution and progressing to leading complicated challenges and mentoring project teams.
Application
Lean originated from the software development industry and is still used today in its original form and various formats such as Kanban, Agile, and Scrum. Teams and organizations across the board use Lean principles to provide more value to customers.
Six Sigma is used in complex contexts where minimizing variability and risk is vital to success. Six Sigma may be used in sectors such as:
- Manufacturing
- Engineering
- Healthcare
- Finance
- Sales
It cannot be applied in every business or context. Small businesses, generally, do not have the resources to adopt Six Sigma.
DMAIC: 5 phases of Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma uses a structured framework called DMAIC. It stands for define, measure, analyze, improve, and control. Let’s walk through the five phases in detail.
Define
The first step is to get crystal clear on what needs fixing. In this phase, you define the goals for your Six Sigma project.
Some key questions to ask:
- What’s the problem we’re solving?
- Who is impacted by this issue? (Customers, teams, stakeholders?)
- How does this problem affect the bottom line?
It’s important to get everyone on the same page, whether they’re part of the project team or affected by the outcome.
Measure
Now that you know the problem, it’s time to figure out how bad it is. You can’t improve what you don’t measure, right? This is where tools like stream mapping (a visual diagram of the process) come in handy to see where things slow down or go wrong.
Ask yourself:
- How long does each step in the process take?
- Where do bottlenecks happen?
- How often do errors or delays occur?
This data will help you see trends, spot weaknesses, and understand the scope of the issue.
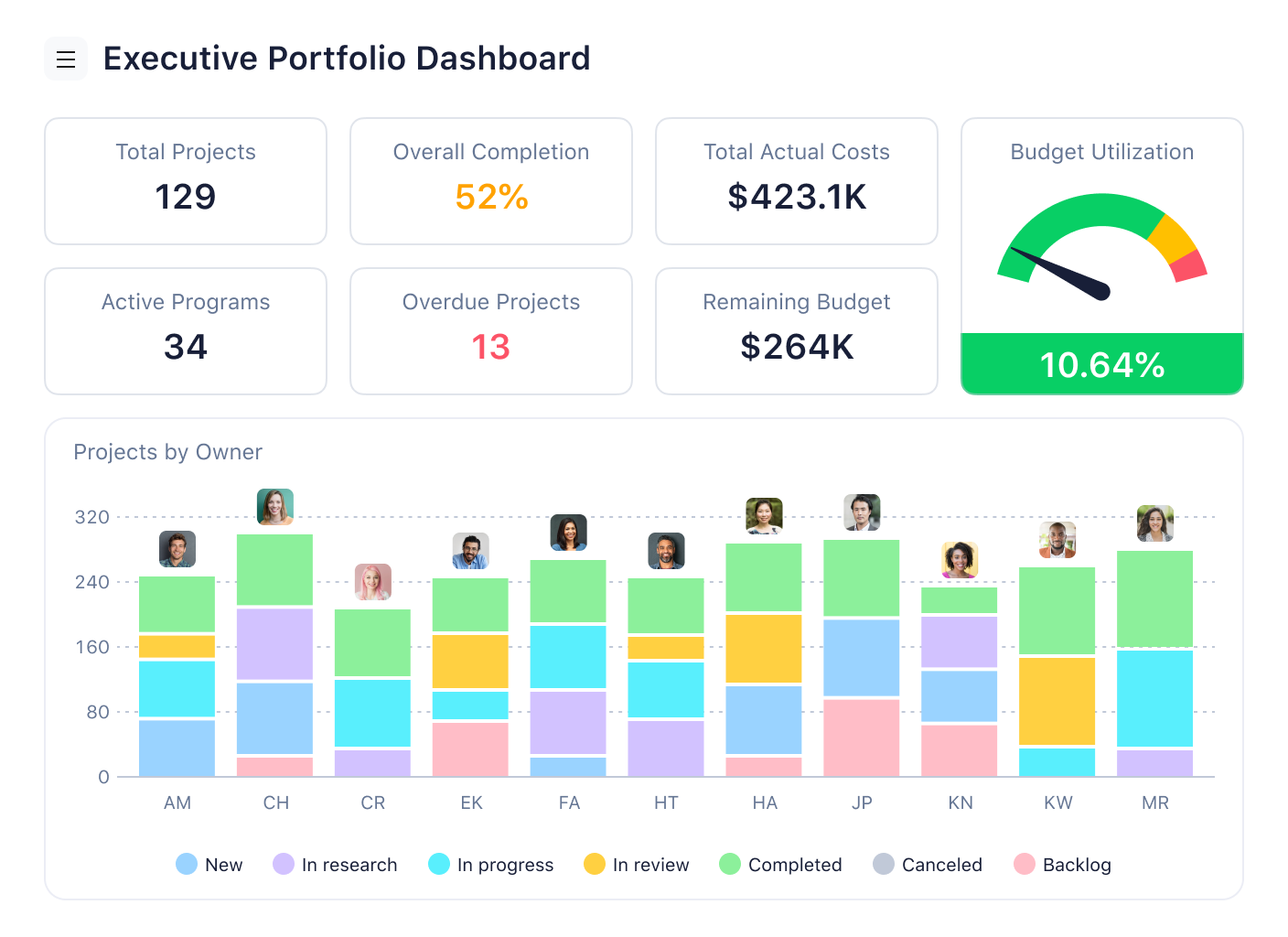
Analyze
Now, it’s time to analyze the data and determine the root cause of waste. Here are some questions to guide you:
- Are there redundant tasks that can be removed?
- Are people unclear about their roles, leading to delays?
- Are tools or technology outdated, creating inefficiencies?
- Are there unnecessary approvals or handoffs slowing things down?
One popular tool used in this phase is the 5 Whys method, where you keep asking “why” until you uncover the real root of the problem.
Improve
This is where you roll up your sleeves and start making changes. It’s also where you brainstorm, test, and implement changes that will improve the process. It’s important to involve the team in this phase because they understand the process best.
Control
The last phase is about making sure the improvements you’ve implemented don’t fall apart over time. After all, what’s the point of fixing something if it’s just going to revert to the old way of working? This phase focuses on maintaining the gains and ensuring the process stays efficient.
Lean manufacturing vs. Six Sigma
In manufacturing, Lean and Six Sigma take slightly different approaches. Lean cuts out waste in the production process. Waste, in this case, could mean time or materials. For example, in a manufacturing process, Lean might reduce waiting times. Six Sigma, on the other hand, prioritizes quality by reducing defects.
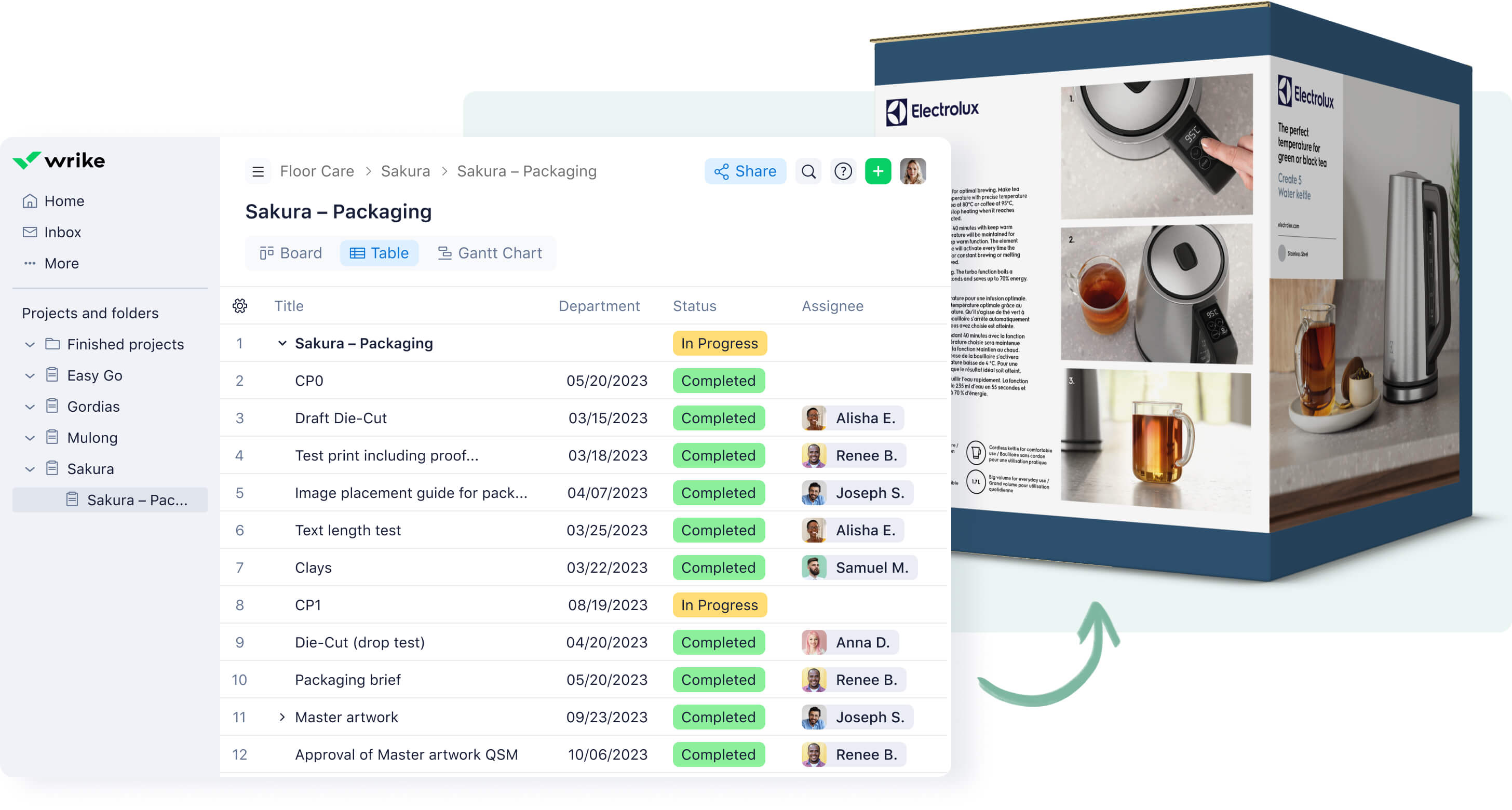
Many manufacturing companies, like Electrolux, now use project management software to create new processes that minimize errors. For example, you can set up an automated workflow and custom request forms in Wrike to streamline your processes while still keeping quality on track.
Belt levels of Lean Six Sigma
In Lean Six Sigma, different belt levels represent varying levels of expertise within the methodology. These certifications are accredited by recognized bodies like the International Association for Six Sigma Certification (IASSC) and the Council for Six Sigma Certification.
Here’s a quick rundown of the belt levels:
Master black belt
This is the top-level expert. Think of them as the strategy leaders and mentors of Lean Six Sigma. They guide others (like black belts and green belts) and make sure the overall strategy aligns with the company’s goals.
Black belt
A black belt is an advanced practitioner who leads Lean Six Sigma projects and teams. They’re in charge of identifying problems, analyzing data, and driving improvements.
Green belt
The green belt is more of a hands-on team player. They work on Lean Six Sigma projects part-time, often juggling their regular job with their improvement work.
Yellow belt
As an entry-level team member in Lean Six Sigma, a yellow belt assists green and black belts in projects and focuses on mastering the basics.
White belt
White belts are newcomers to Lean Six Sigma. They get introduced to the methodology and its principles, helping with smaller tasks and learning how the system works in practice.

Lean vs Six Sigma: Which is the better option for you?
Choosing between Lean or Six Sigma? The decision will depend on your goals. Lean can be a good fit for your company if you need a simple, continuous framework to drive improvement and growth. Six Sigma may be better if you want to minimize unpredictability and improve efficiency in a more complicated setting.
You can combine Six Sigma and Lean to create a hybrid technique known as Lean Six Sigma to get the best of both methodologies. Lean Six Sigma is effective in helping organizations reduce costs and waste while enhancing the speed and quality of operations and output.
To make the most of these frameworks, workflow management software like Wrike can support your Lean and Six Sigma projects. Explore features like custom dashboards and time tracking to help you keep an eye on potential waste areas and identify areas to boost performance.

Artem Gurnov
Artem is a Director of Account Development at Wrike. He previously held the role of Project Manager, overseeing a team of customer success managers (CSMs). Over the years of building teams and scaling business processes, he has successfully deployed multiple projects, from automating client outreach to setting up work prioritization tools for sales reps and CSMs.