What Is Lean Six Sigma in Project Management?
Lean Six Sigma is a hybrid methodology that combines two popular approaches to process improvement: Lean and Six Sigma. Together, they help teams deliver higher-quality results without wasting resources. Understanding each of these concepts will help you better grasp how project management in Lean Six Sigma actually works.
In this article, we’ll look at the Lean Six Sigma project management methodology, including its techniques and importance. You’ll learn how this hybrid method can help improve the quality of your projects. We’ll also show you how project management platforms like Wrike can complement Lean Six Sigma by helping teams stay organized, track progress, and collaborate more effectively.
Short on time? Here’s a quick video that explains Lean Six Sigma in project management.

Video transcript:
What is Lean Six Sigma project management? Lean Six Sigma project management is a hybrid methodology that combines the characteristics of Lean and Six Sigma to help project managers improve their processes. Let’s break it down into two components.
As the name suggests, Lean project management is all about reducing waste. Project managers identify waste areas by creating a work breakdown process. This helps them to avoid activities that add little value to a project. They also aim to reduce levels of excess inventory. The overall goal of Lean is to do more with less. Teams work with the bare minimum of materials required to get their job done. If successful, they spend less time, money, and manpower, meaning the project’s processes are far more efficient.
Six Sigma project management is a little different. Though it is also a process-based methodology, it focuses on statistics to improve the quality of a team’s processes. Six Sigma teams identify production defects and variations and aim to reduce them as much as possible. Teams can achieve a Six Sigma rating if 99.99966% of their project opportunities are defect-free.
The concept of Lean Six Sigma was born in 2001 in the book, “Leaning into Six Sigma: The Path to Integration of Lean Enterprise and Six Sigma,” written by Barbara Wheat, Chuck Mills, and Mike Carnell. The authors introduced this fusion of methodologies as a solution for manufacturing plant managers looking to reduce their production cycle time.
So, now you know the background of Lean Six Sigma project management. But how does it actually work? By combining the zero-waste mentality of Lean with the zero-defects ideology of Six Sigma, Lean highlights any unwanted variation in a project’s processes, and Six Sigma reduces it with a series of improvements, working together to provide a better consumer experience.
When figuring out how to use Lean Six Sigma, it’s important to start with Lean. First, identify your waste areas and trim any excess fat. Then, you can refine your processes with the Six Sigma method of DMAIC. DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It is a straightforward method that helps teams deal with problems that may arise throughout a project.
Though both Lean and Six Sigma originated in the manufacturing field, the principles of Lean Six Sigma project management can be applied to any industry. It has gained popularity among software developers who use it in their quest to track and fix bugs. There are many advantages to using Lean Six Sigma project management. These include:
- Reduced costs: Lean Six Sigma teams generate less waste, so they save money on production costs, such as materials and storage fees. By detecting defects early in the project, they can also eliminate the unnecessary costs associated with faulty products.
- Improved processes: Cutting down on process variation means teams gain more control over their projects, enabling them to standardize their workflow. This leads to a more streamlined, efficient approach.
- Better employee engagement: Lean Six Sigma project management encourages team members to take accountability for solving problems. Project managers trust teams to carry out process improvements, meaning they have an increased sense of ownership over their projects.
However, there are some disadvantages to Lean Six Sigma project management:
- Complexity: Because Lean Six Sigma requires prior knowledge of two methodologies, teams cannot adopt it as easily as they could, say, an Agile framework such as Scrum.
- Resource-intensive: Lean Six Sigma project management takes a lot of time as teams strive to follow the principles of waste elimination and defect reduction. This can lead to increased workloads and, in extreme cases, burnout.
- Potential customer loss: In your efforts to reduce defects and improve quality, your organization may opt for more expensive materials, raising the price of your product. This may deter customers who aren’t willing to spend extra, leading them to choose a cheaper competitor.
So now you know the basics of Lean Six Sigma project management. If your team is familiar with both Lean and Six Sigma, it could be exactly what you need to help you improve your project processes. Whatever methodology you choose, Wrike can help you streamline your projects and boost efficiency. Our project management features include Kanban boards, time tracking tools, automated reports, and much more. Want to learn how Wrike can help you kick-start your Lean Six Sigma project management? Start your free two-week trial today.
Lean Six Sigma vs. Six Sigma
- What is Lean? Lean project management is all about reducing waste. The goal is to do more with less. Teams identify waste areas so that they can avoid any project activities that offer little or no value. The result is more efficient processes that require less time, money, and effort.
- What is Six Sigma? Six Sigma methodology focuses on using statistics to improve the quality of a team’s processes. It takes a magnifying glass to processes to identify any production defects and variations. Some people even get a Six Sigma certification to prove their knowledge in identifying and removing defects.
When you put the two together, you get Lean Six Sigma. With this approach, Lean first calls attention to any unwanted process variations, while Six Sigma steps in and uses a series of improvements to reduce those variations. How? Six Sigma uses the DMAIC acronym, which stands for:
- Define
- Measure
- Analyze
- Improve
- Control
Let’s break down each of these in detail.
Define
In this phase, teams:
- Clearly outline the goal (what needs improvement)
- Determine the project scope
- Establish measurable goals to track progress and milestones

This phase generally sets the foundation by aligning everyone on the goals and ensuring the issue is well understood.
Measure
After defining the problem, teams need to understand the current state of the process. This step provides the data and insight necessary to identify areas for continuous improvement.
Analyze
Now that you’ve collected the data, it’s time to figure out what’s causing the problem. This step is about problem solving — going beyond the surface to understand what’s going wrong. To do this, you should:
- Look for patterns or trends in the data that highlight where things go wrong
- Focus on finding the root causes, not just the symptoms of the issue
- Use tools like flowcharts to connect the dots
- Eliminate processes that don’t add value
By the end of this phase, you’ll have a clear understanding of what’s broken and what needs to change.
Improve
Now that you know what’s wrong, you can take action to improve process flow and make meaningful changes. During this phase, teams focus on eliminating waste, improving efficiency, and enhancing the bottom line.
Control
Finally, once improvements are made, it’s important to ensure they stick. The control phase helps you maintain your progress and keep improving over time. Control isn’t about rigid rules but creating systems that make the new, improved process part of the team’s routine.
To put this all in even simpler terms, Lean highlights the holes in the bucket, and Six Sigma patches them.
Lean Six Sigma techniques
How do you identify what’s slowing down your team? Lean Six Sigma techniques do exactly that. Here are some of the techniques you should keep in mind:
Root cause analysis
When problems keep arising, addressing surface-level issues won’t cut it. One of the most effective tools here is the “5 Whys” method, which helps you peel back the layers of a problem.
- Ask “why” the issue occurred.
- Follow up with another “why” based on the first answer.
- Repeat this process until you find the root cause.
For example:
- Why are projects often delayed? Because team members miss deadlines.
- Why do team members miss deadlines? Because they don’t have clear priorities.
- Why don’t they have clear priorities? Because there’s no system to manage task dependencies.
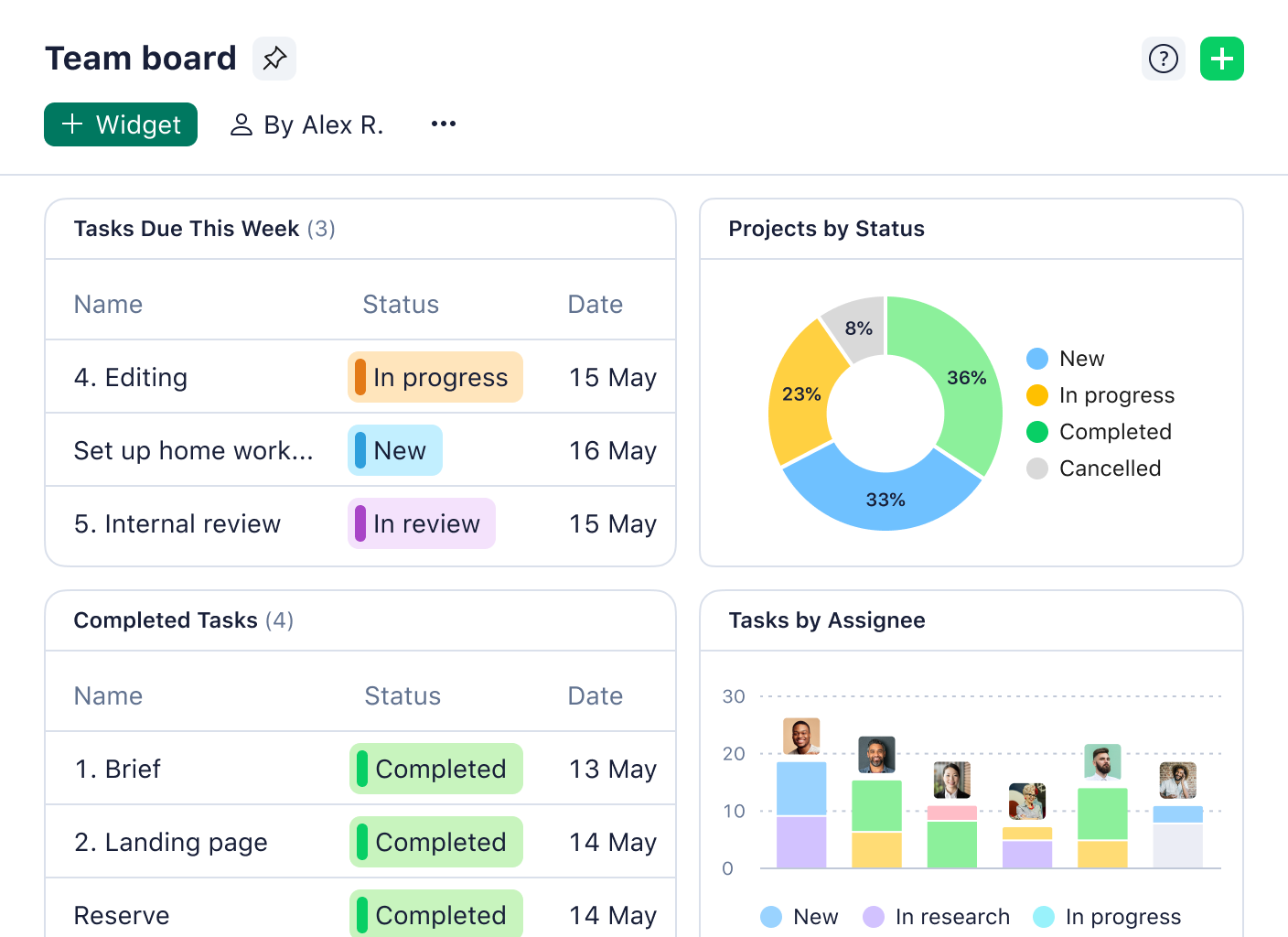
This method ensures that you’re solving and addressing the core issues. You can use Wrike’s dashboards to monitor team activity and resource allocation so you can identify patterns that contribute to bottlenecks.

SIPOC diagrams
Before diving into the finer details of a project, it’s helpful to understand the big picture. SIPOC diagrams are perfect for this, providing a high-level overview of your workflow by focusing on:
- Suppliers: Who provides the inputs for your process?
- Inputs: What materials, information, or resources do you need?
- Process: What are the major steps in your workflow?
- Outputs: What does the process deliver, and in what form?
- Customers: Who benefits from or uses the outputs?
This technique ensures that every part of your Lean Sigma project aligns with your goals.
Kaizen
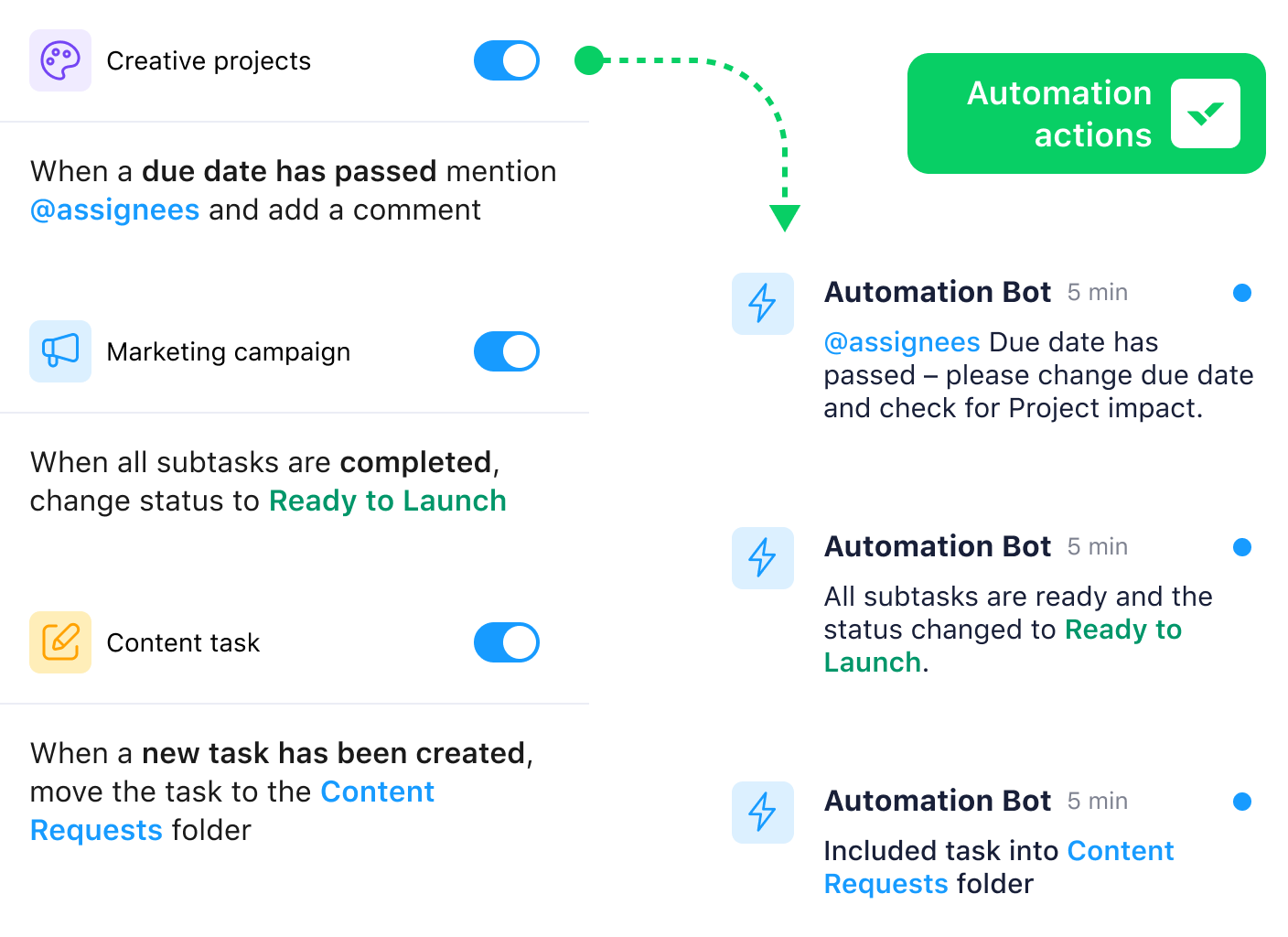
Kaizen is all about making small, incremental improvements over time rather than tackling everything at once. This way, you can have a structured method that focuses on eliminating inefficiencies.
Instead of manually making these changes, you can set up an automated workflow in Wrike that ensures every improvement becomes part of your team’s routine.

Lean Six Sigma belt levels
Lean Six Sigma uses a structured hierarchy of expertise known as ’’belt level’’ to guide teams through the process improvement journey. Let’s break down what each level means and how they contribute to successful Lean Six Sigma projects.
White belt
White belts are the starting point in Lean Six Sigma. They’re introduced to the fundamental concepts and help out in smaller ways, like supporting teams with simple tasks or learning the lingo.
Yellow belt
A yellow belt is an entry-level team member with a basic understanding of Lean Six Sigma principles and project management. Yellow belt holders help identify areas of extra processing (activities that do not add value).
Green belt
Green belts have more advanced training in Six Sigma Lean project management and typically take on larger roles in projects. They collaborate closely with team members to drive waste reduction efforts.
Black belt
Black belts are full-time Lean Six Sigma experts who lead complex, high-impact projects. Their deep understanding of the methodology enables them to drive organizational change. Black belts also provide training and mentorship to green and yellow belts.
Master black belt
At the top of the hierarchy is the master black belt, an expert who oversees the entire Lean Six Sigma program within an organization. A master black belt aligns projects with organizational goals, such as optimizing Lean manufacturing processes.

Lean Six Sigma certifications
Thinking about getting certified in Lean Six Sigma? Earning a Lean Six Sigma certification positions you as a valuable asset in any organization. Certification is tied to the belt levels and reflects your ability to lead, support, or strategize Lean Six Sigma projects.
Let’s look at what certification involves and what you can expect in terms of cost and training.
Level | Training duration | Cost |
White belt | 1 hour | Free |
Yellow belt | 1-3 weeks | $99 |
Green belt | 2-7 weeks | $159 |
Black belt | 1-3 months | $229 |
Master black belt | 4-6 months | $665 |
Importance of Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma is a well-recognized framework that focuses on eliminating inefficiencies and improving quality. This combination helps teams save time, reduce costs, and consistently deliver better results.
To sum it up, Lean Six Sigma combines the zero-waste ideology of Lean and the zero-defects ideology of Six Sigma to create a new, hybrid approach that ultimately helps teams get better work across the finish line in less time.
Is Lean Six Sigma right for your team?
Lean Six Sigma got its start in manufacturing, but it has since expanded to virtually every other industry. Despite its popularity, it’s not the default right choice to help your project team work more effectively and efficiently. To make an informed decision, you should consider all the potential benefits of Lean Six Sigma as well as the drawbacks.
Advantages of Lean Six Sigma
-
Lower costs: Because there’s less waste and defect-free products, teams can save money.
- Improved processes: With more control and fewer variations, processes are far more streamlined and consistent.
- Better employee engagement: With Lean Six Sigma, teams are accountable for solving problems. Project managers trust them to carry out any process improvements, and that level of autonomy can boost their enthusiasm and engagement.
Disadvantages of Lean Six Sigma:
- Complexity: To do it well, it requires prior knowledge of two different project methodologies. So, it can feel a little daunting and is not as easily adopted as other approaches.
- Resource-intensive: It’s not a fast-moving approach and it takes a lot of time to follow the principles. Teams will likely also have increased workloads as they move through the process.
- Potential customer loss: To reduce defects, you might have to opt for more expensive resources and materials. That can raise the price of your end product and even lead to customer churn.
Execute Lean Six Sigma principles in Wrike
Now that you’ve learned about Lean Six Sigma and how it can help you identify inefficiencies, the next step is making it happen.
But even the best methodology needs the right tools to bring it to life. That’s why you should consider using Wrike. Lean Six Sigma focuses on driving results, and Wrike gives you the flexibility and tools to achieve those results faster.
With Wrike, you can:
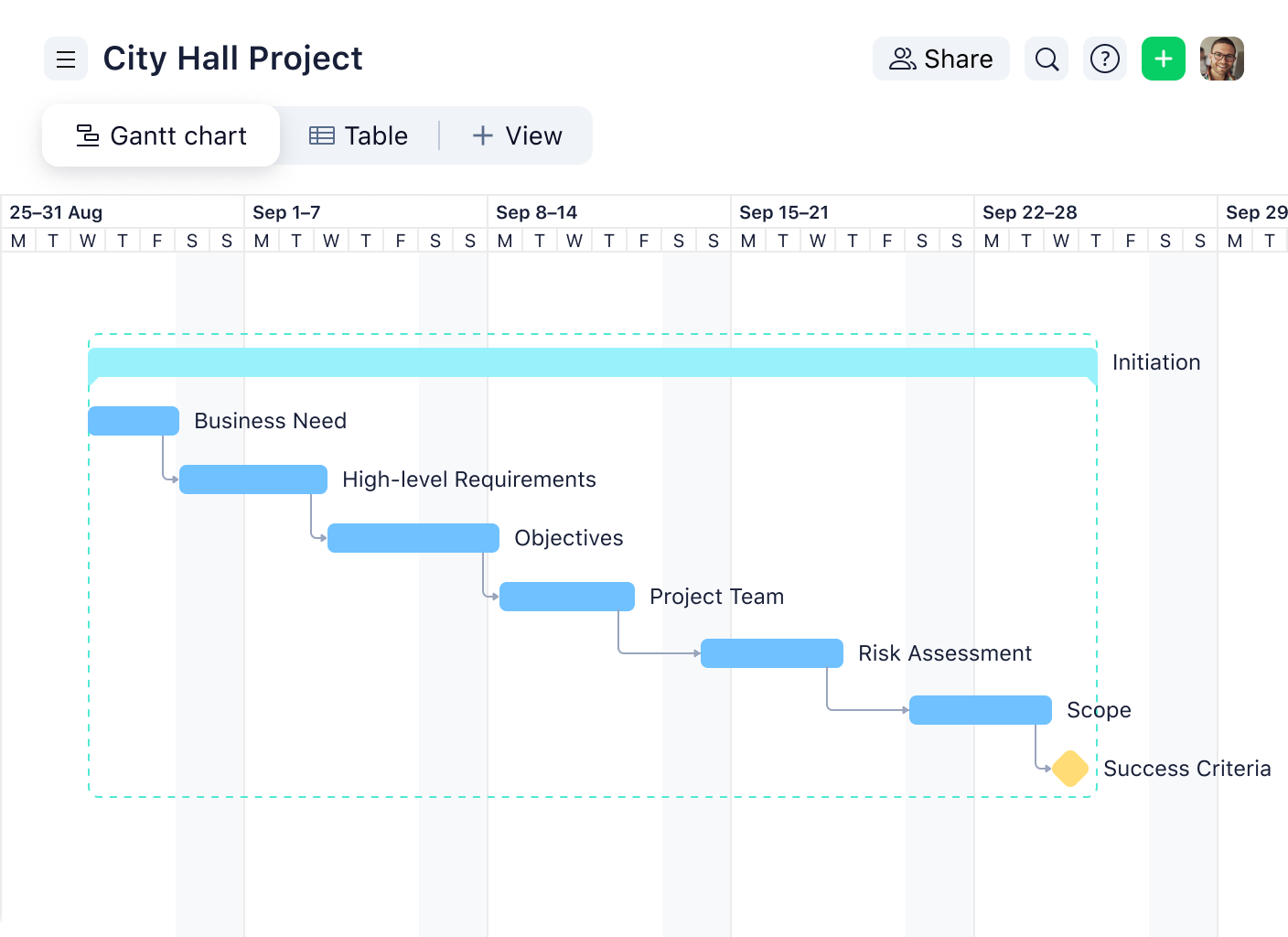
- Visualize your process with Gantt charts and spot bottlenecks
- Collaborate with your team on shared, customized workspaces so everyone is aligned
- Monitor progress, track key metrics, and set goals in real time
- Tailor templates based on your project needs
- Use Kanban boards to map out your process and identify areas for improvement
Ready to bring your Lean Six Sigma projects to life? Start your two-week free trial with Wrike.

Artem Gurnov
Artem is a Director of Account Development at Wrike. He previously held the role of Project Manager, overseeing a team of customer success managers (CSMs). Over the years of building teams and scaling business processes, he has successfully deployed multiple projects, from automating client outreach to setting up work prioritization tools for sales reps and CSMs.